An exoplanet is a planet that orbits another star other than the Sun; since 1988, almost 6,000 of them have been confirmed. This catalogue provides a visual way to visualise exoplanets in their solar systems, together with their habitable zones. The data comes from the NASA Exoplanet Archive and it only includes all the confirmed exoplanets since August 2025. For more information about exoplanets, you can check the main article here.
For licensing and enquires, contact ![]() .
.
- ¶ Solar System
- ¶ Exoplanetary Systems
- ¶ Very large (x100)
- ¶ Large (x10)
- ¶ Medium
- ¶ Small
- ¶ Very small
- ¶ Notes
Solar System
Exoplanetary Systems
Very large
The size of those exoplanetary systems are scaled down 100 times compared to the Solar System, to allow them to be drawn correctly. Due to their sheer size, the orbital periods of those planets are measured in decades or even centuries; they are moving 100 times faster.
Large
The size of those exoplanetary systems are scaled down 10 times compared to the Solar System, to allow them to be drawn correctly, and moving 10 times faster.
Medium
The size of those exoplanetary systems are scaled down 1 times compared to the Solar System, to allow them to be drawn correctly.
Small
Very small
Notes
📏 Orbital parameters
- Distance:
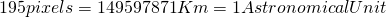 ;
; - Planets: Confirmed planets from the NASA Exoplanet Archive (last update: December 2015); only planets with known orbital period, semi-axis major and radius are shown;
- Orbits:
 ; orbits with unknown eccentricity in light grey. Initial positions are synchronised so that when they hit zero degrees, they transit in front of their stars, from the Earth’s perspective.
; orbits with unknown eccentricity in light grey. Initial positions are synchronised so that when they hit zero degrees, they transit in front of their stars, from the Earth’s perspective.
🪐 Planetary parameters
- Planet size:
 (square root):
(square root):
- Temperature: planetary equilibrium temperature goes from
 (−273.15°C) to
(−273.15°C) to 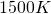 (=1226.85°C); green area from
(=1226.85°C); green area from  (0°C) to
(0°C) to  (40°C):
(40°C):
- Habitable zone: inner bound:
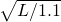 Astronomical Units, outer bound:
Astronomical Units, outer bound:  Astronomical Units (
Astronomical Units (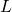 is the star luminosity relative to the Sun); habitable zones are calculated taking into account only the first orbit:
is the star luminosity relative to the Sun); habitable zones are calculated taking into account only the first orbit:
⭐ Star parameters
- Stars: for systems with multiple stars, only the primary one is visualised; stars are always assumed to be in the right focus of elliptical orbits;
- Star size:
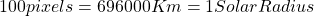 (square root); stars with unknown radius are represented as
(square root); stars with unknown radius are represented as  ;
; - Stellar type:
📄 Nomenclature list
- 2MASS: Two Micron All-Sky Survey
- BD: Bonner Durchmusterung catalogue
- BLG: Bulge field (Galactic center microlensing targets)
- CD: Córdoba-Durchmusterung catalogue
- CFBDSIR: Canada-France Brown Dwarf Survey InfraRed
- CFHTWIR: Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Wide-field Infrared
- COCONUTS: COol Companions ON Ultrawide orbiTS
- CoRoT: COnvection ROtation and planetary Transits project by CNES & ESA
- CT: Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory
- DE: Delisle-Evans catalog
- DENIS-P: Deep Near Infrared Survey (Proper motion objects)
- DMPP: Dispersed Matter Planet Project
- EPIC: Ecliptic Plane Input Catalog (K2 / Kepler mission targets)
- Gaia: ESA’s Gaia mission
- Gl/GJ: Gliese / Gliese–Jahreiß Catalog (nearby stars)
- GSC: Guide Star Catalog
- HAT: Hungarian Automated Telescope Network by Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
- HD: Henry Draper Catalog
- HIP: High Accuracy Radial velocity Planet Searcher for the Northern hemisphere (HARPS-N)
- HIP: Hipparcos Catalog
- HR: Bright Star Catalog (Harvard Revised)
- IRAS: Infrared Astronomical Satellite
- K2: Kepler spacecraft by NASA, “Second Light” mission;
- KELT: Kilodegree Extremely Little Telescope survey
- Kepler: Kepler spacecraft by NASA
- KIC: Kepler Input Catalog
- KMT: Korea Microlensing Telescope Network
- KOBE: K-dwarfs Orbited By habitable Exoplanets
- KOI: Kepler Object of Interest via Kepler spacecraft
- LHS: Luyten Half-Second proper motion stars
- LSPM: Lépine & Shara Proper Motion catalog
- LTT: Luyten Two-Tenths catalog
- Lupus: Lupus star-forming region
- MASCARA: Multi-site All-Sky CAmeRA project
- MOA: Microlensing Observations in Astrophysics
- MWC: Mount Wilson Catalog (emission-line stars)
- MXB: X-ray binary catalog (Mit X-ray Binaries)
- NGC: New General Catalogue (star clusters, nebulae, galaxies)
- NGTS: Next-Generation Transit Survey (Paranal Observatory, Chile)
- NGTS: Next-Generation Transit Survey
- NSVS: Northern Sky Variability Survey
- OGLE: Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment
- PDS: Pico dos Dias Survey (young stars, disks)
- PH: Planet Hunters (citizen science project for Kepler data)
- POTS: Planetary Transit and Oscillations of Stars (PLATO)
- PSR: Pulsar
- Qatar: Qatar Exoplanet Survey Telescope
- Ross: Frank Elmore Ross’s proper motion catalog
- ROXs: Rho Ophiuchi X-ray stars
- SWEEPS: Sagittarius Window Eclipsing Extrasolar Planet Search (Hubble)
- TAP: Transit and Photometry Survey
- TOI: TESS Objects of Interest, via TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite)
- UCAC3: USNO CCD Astrograph Catalog (3rd version)
- UKIRT: UK Infrared Telescope
- USco: Upper Scorpius association
- VHS: VISTA Hemisphere Survey
- WASP: Wide Angle Search for Planets;
- Wendelstein: Wendelstein Observatory survey
- WISE: Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer
- Wolf: Max Wolf’s catalog of high proper motion stars
- WTS: WFCAM (Wide Field Camera Project) Transit Survey
- XO: XO Telescope
- YSES: Young Suns Exoplanet Survey
- ZTF: Zwicky Transient Facility


Leave a Reply